聚簇索引Clustering Key
本文為您介紹在Hologres中聚簇索引Clustering Key使用的相關(guān)內(nèi)容。
Clustering Key介紹
Hologres會按照聚簇索引在文件內(nèi)對數(shù)據(jù)進行排序,建立聚簇索引能夠加速在索引列上的范圍和過濾查詢。設(shè)置Clustering Key的語法如下,需要建表時指定。
-- Hologres V2.1版本起支持的語法
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (...) WITH (clustering_key = '[<columnName>[,...]]');
-- 所有版本支持的語法
BEGIN;
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (...);
CALL set_table_property('<table_name>', 'clustering_key', '[<columnName>{:asc} [,...]]');
COMMIT;參數(shù)說明:
參數(shù) | 說明 |
table_name | 設(shè)置聚簇索引的表名稱。 |
columnName | 設(shè)置聚簇索引的字段名稱。 |
使用建議
Clustering Key主要適用于點查以及范圍查詢的場景,對于過濾操作有比較好的性能提升,即對于
where a = 1或者where a > 1 and a < 5的場景加速效果比較好。可以同時設(shè)置Clustering Key和Bitmap Column以達到最佳的點查性能。Clustering Key具備左匹配原則,因此一般不建議設(shè)置Clustering Key超過兩個字段,否則適用場景受限。Clustering Key是用于排序,所以Clustering Key里的列組合是有先后關(guān)系的,即排在前面列的排序優(yōu)先級高于后面的列。
指定Clustering Key字段時,可在字段名后添加
:asc來構(gòu)建索引時的排序方式。排序方式默認為asc,即升序。Hologres V2.1以前版本不支持設(shè)置構(gòu)建索引時的排序方式為降序(desc),如果設(shè)置了降序,無法命中Clustering Key,導(dǎo)致查詢性能不佳;從V2.1版本開始,開啟如下GUC后支持設(shè)置Clustering Key為desc,但僅支持Text、Char、Varchar、Bytea、Int等類型的字段,其余數(shù)據(jù)類型的字段暫不支持設(shè)置Clustering Key為desc。set hg_experimental_optimizer_enable_variable_length_desc_ck_filter = on;對于行存表,Clustering Key默認為主鍵 (Hologres V0.9之前版本默認不設(shè)置)。如果設(shè)置和主鍵不同的Clustering Key,那么Hologres會為這張表生成兩個排序(Primary Key排序和Clustering Key排序),造成數(shù)據(jù)冗余。
使用限制
如需修改Clustering Key,請重新建表并導(dǎo)入數(shù)據(jù)。
Clustering Key必須為not nullable的列或者列組合。Hologres V1.3.20~1.3.27版本支持Clustering Key為nullable,從V1.3.28版本開始不支持Clustering Key為nullable,為nullable的Clustering Key可能會影響數(shù)據(jù)正確性,如果業(yè)務(wù)有強需求設(shè)置Clustering Key為null,可以在SQL前添加如下參數(shù)。
set hg_experimental_enable_nullable_clustering_key = true;不支持將Float、Float4、Float8、Double、Decimal(Numeric)、Json、Jsonb、Bit、Varbit、Money、Time With Time Zone及其他復(fù)雜數(shù)據(jù)類型的字段設(shè)置為Clustering Key。
Hologres V2.1以前版本不支持設(shè)置構(gòu)建索引時的排序方式為降序(
desc),如果設(shè)置了降序,無法命中Clustering Key,導(dǎo)致查詢性能不佳;從V2.1版本開始,開啟如下GUC后支持設(shè)置Clustering Key為desc,但僅支持Text、Char、Varchar、Bytea、Int等類型的字段,其余數(shù)據(jù)類型的字段暫不支持設(shè)置Clustering Key為desc。set hg_experimental_optimizer_enable_variable_length_desc_ck_filter = on;對于列存表,Clustering Key默認為空,需要根據(jù)業(yè)務(wù)場景顯式指定。
在Hologres中,每個表只能設(shè)置一組Clustering Key。即建表的時候只能使用
call命令一次,不能執(zhí)行多次,如下示例:V2.1版本起支持的建表語法:
--正確示例 CREATE TABLE tbl ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( clustering_key = 'a,b' ); --錯誤示例 CREATE TABLE tbl ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( clustering_key = 'a', clustering_key = 'b' );所有版本支持的建表語法:
--正確示例 BEGIN; CREATE TABLE tbl (a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL); CALL set_table_property('tbl', 'clustering_key', 'a,b'); COMMIT; --錯誤示例 BEGIN; CREATE TABLE tbl (a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL); CALL set_table_property('tbl', 'clustering_key', 'a'); CALL set_table_property('tbl', 'clustering_key', 'b'); COMMIT;
技術(shù)原理
Clustering Key在物理存儲上是指在文件內(nèi)進行排序,默認為升序(asc),可以通過下圖理解Clustering Key的布局概念。
邏輯布局。
Clustering Key查詢具備左匹配原則,不匹配則無法使用Clustering Key查詢加速。如下場景示例將為您說明Hologres中Clustering Key的邏輯布局。
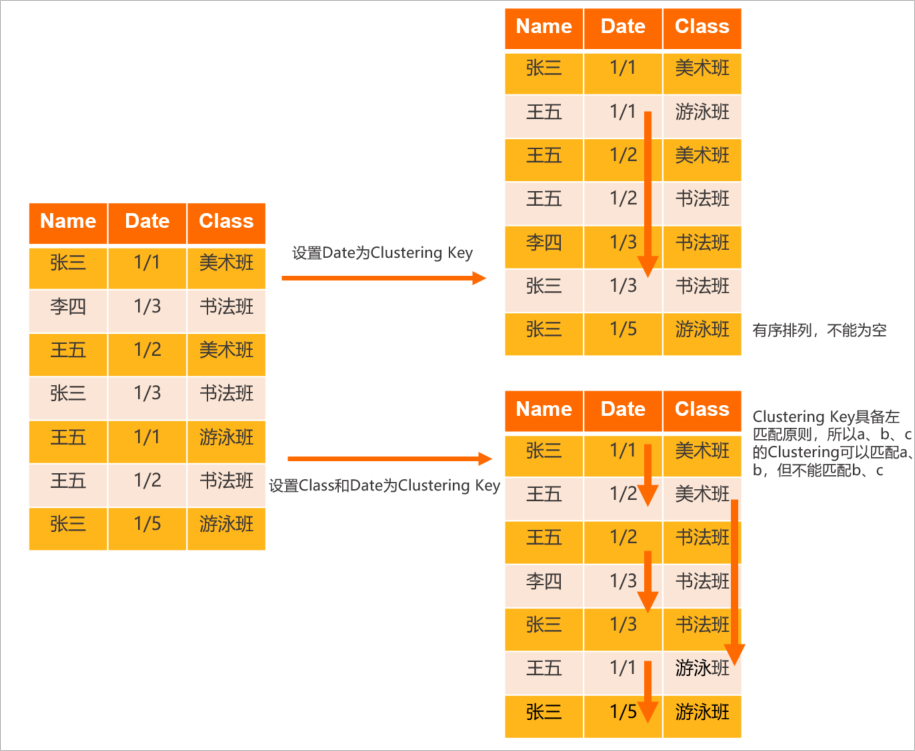
準備一張表,其字段分別包括Name、Date、Class。
設(shè)置Date為Clustering Key,會將表內(nèi)的數(shù)據(jù)按照Date進行排序。
設(shè)置Class和Date為Clustering Key,會對表先按照Class排序后再按照Date進行排序。
設(shè)置不同的字段為Clustering Key,其最終的呈現(xiàn)結(jié)果也不同,具體如下圖所示。
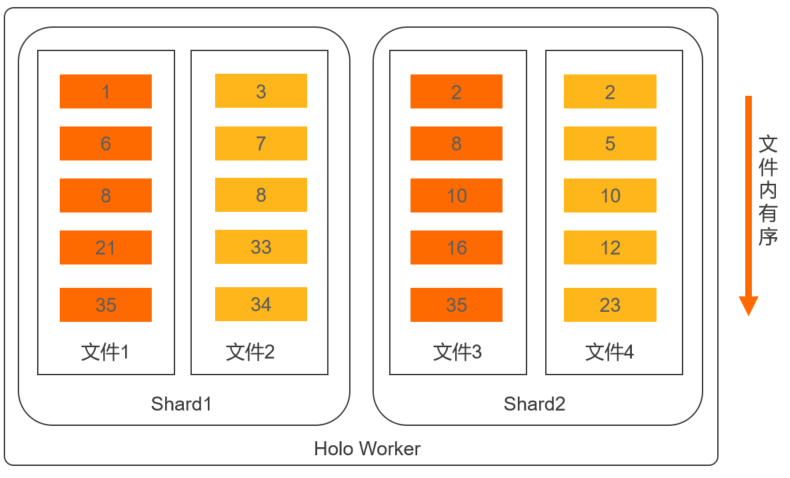
物理存儲布局。
Clustering Key的物理存儲布局如下圖所示。
通過Clustering Key的布局原理可以看出:
Clustering Key適合范圍過濾的場景。比如
where date= 1/1或者where a > 1/1 and a < 1/5的場景加速效果比較好。Clustering Key查詢具備左匹配原則,不匹配則無法利用上Clustering Key查詢加速。即假設(shè)設(shè)置
a,b,c三列為Clustering Key,如果是查a,b,c或者查a,b可以命中Clustering Key;如果查a,c只有a可以命中Clustering Key;如果查b,c則無法命中Clustering Key。
如下示例,設(shè)置uid,class,date三列為Clustering Key。
V2.1版本起支持的語法:
CREATE TABLE clustering_test ( uid int NOT NULL, name text NOT NULL, class text NOT NULL, date text NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (uid) ) WITH ( clustering_key = 'uid,class,date' ); INSERT INTO clustering_test VALUES (1,'張三','1','2022-10-19'), (2,'李四','3','2022-10-19'), (3,'王五','2','2022-10-20'), (4,'趙六','2','2022-10-20'), (5,'孫七','2','2022-10-18'), (6,'周八','3','2022-10-17'), (7,'吳九','3','2022-10-20');所有版本支持的語法:
BEGIN; CREATE TABLE clustering_test ( uid int NOT NULL, name text NOT NULL, class text NOT NULL, date text NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (uid) ); CALL set_table_property('clustering_test', 'clustering_key', 'uid,class,date'); COMMIT; INSERT INTO clustering_test VALUES (1,'張三','1','2022-10-19'), (2,'李四','3','2022-10-19'), (3,'王五','2','2022-10-20'), (4,'趙六','2','2022-10-20'), (5,'孫七','2','2022-10-18'), (6,'周八','3','2022-10-17'), (7,'吳九','3','2022-10-20');
只查
uid列,可以命中Clustering Key。SELECT * FROM clustering_test WHERE uid > '3';通過查看執(zhí)行計劃(explain SQL),如下所示執(zhí)行計劃中有
Cluster Filter算子,表明命中了Clustering Key,查詢加速。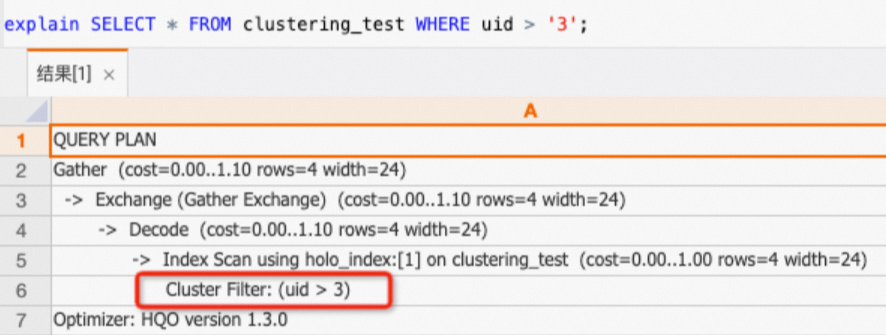
查
uid,class列,可以命中Clustering Key。SELECT * FROM clustering_test WHERE uid = '3' AND class >'1' ;通過查看執(zhí)行計劃(explain SQL),如下所示執(zhí)行計劃中有
Cluster Filter算子,表明命中了Clustering Key,查詢加速。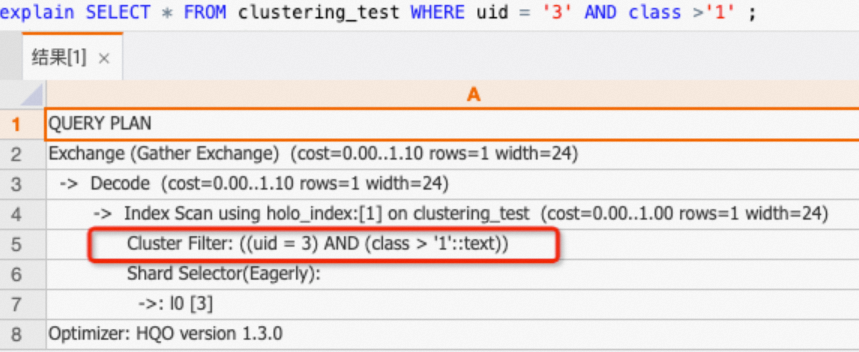
查
uid,class,date三列可以命中Clustering Key。SELECT * FROM clustering_test WHERE uid = '3' AND class ='2' AND date > '2022-10-17';通過查看執(zhí)行計劃(explain SQL),如下所示執(zhí)行計劃中有
Cluster Filter算子,表明命中了Clustering Key,查詢加速。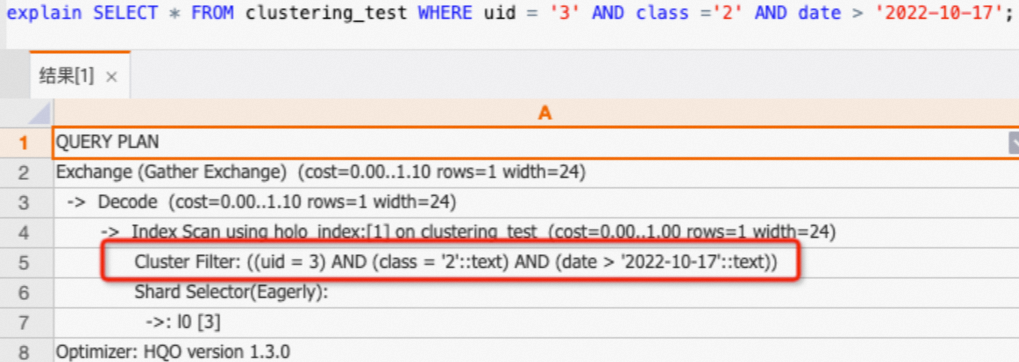
查
uid,date兩列,不符合左匹配原則,因此只有uid可以命中Clustering Key,date則是走普通過濾。SELECT * FROM clustering_test WHERE uid = '3' AND date > '2022-10-17';通過查看執(zhí)行計劃(explain SQL),如下所示執(zhí)行計劃中只有uid列有
Cluster Filter算子。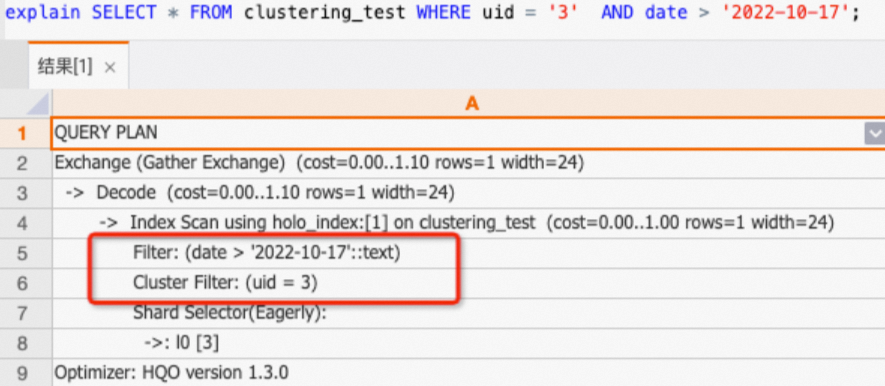
只查
class,date兩列,不符合左匹配原則,都無法命中Clustering Key。SELECT * FROM clustering_test WHERE class ='2' AND date > '2022-10-17';通過查看執(zhí)行計劃(explain SQL),如下所示執(zhí)行計劃中沒有
Cluster Filter算子,表明未命中Clustering Key。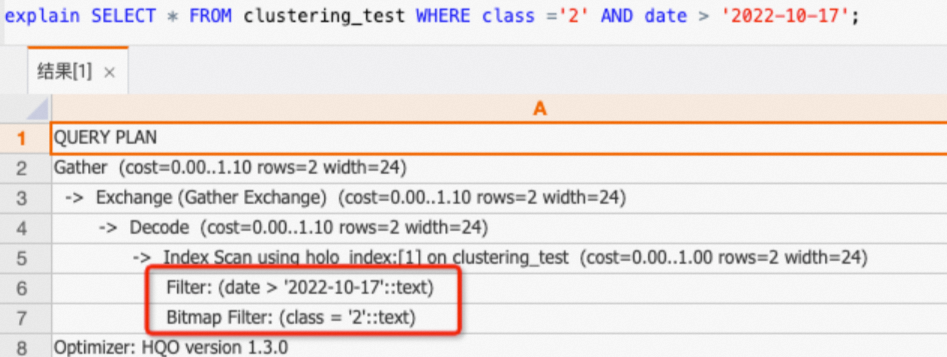
使用示例
示例1:命中Clustering Key的場景。
V2.1版本起支持的語法:
CREATE TABLE table1 ( col1 int NOT NULL, col2 text NOT NULL, col3 text NOT NULL, col4 text NOT NULL ) WITH ( clustering_key = 'col1,col2' ); --如上的建表sql,query可以被加速的情況如下: -- 可加速 select * from table1 where col1='abc'; -- 可加速 select * from table1 where col1>'xxx' and col1<'abc'; -- 可加速 select * from table1 where col1 in ('abc','def'); -- 可加速 select * from table1 where col1='abc' and col2='def'; -- 不可加速 select col1,col4 from table1 where col2='def';所有版本支持的語法:
begin; create table table1 ( col1 int not null, col2 text not null, col3 text not null, col4 text not null ); call set_table_property('table1', 'clustering_key', 'col1,col2'); commit; --如上的建表sql,query可以被加速的情況如下: -- 可加速 select * from table1 where col1='abc'; -- 可加速 select * from table1 where col1>'xxx' and col1<'abc'; -- 可加速 select * from table1 where col1 in ('abc','def'); -- 可加速 select * from table1 where col1='abc' and col2='def'; -- 不可加速 select col1,col4 from table1 where col2='def';
示例2:Clustering Key設(shè)置為asc/desc。
V2.1版本起支持的語法:
CREATE TABLE tbl ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( clustering_key = 'a:desc,b:asc' );所有版本支持的語法:
BEGIN; CREATE TABLE tbl ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ); CALL set_table_property('tbl', 'clustering_key', 'a:desc,b:asc'); COMMIT;
高級調(diào)優(yōu)手段
和傳統(tǒng)數(shù)據(jù)庫(MySQL或SQLServer)中的聚簇索引不同,Hologres的排序僅做到了文件內(nèi)的排序,并非是全表數(shù)據(jù)的排序,因此在Clustering Key上做order by操作仍然有一定的代價。
Hologres從V1.3版本開始針對Clustering Key的場景使用做了較多的性能優(yōu)化,實現(xiàn)在使用Clustering Key時有更好的性能,主要包含如下兩個場景優(yōu)化。如果您的版本低于1.3版本,請您使用自助升級或加入Hologres釘釘交流群反饋,詳情請參見如何獲取更多的在線支持?。
針對Clustering Keys做Order By場景
在Hologres中,文件內(nèi)是按照Clustering Keys定義排序的,但在V1.3版本之前,優(yōu)化器無法利用文件內(nèi)的Clustering Keys有序性生成最優(yōu)執(zhí)行計劃;同時經(jīng)過Shuffle節(jié)點時也無法保障數(shù)據(jù)有序輸出(多路歸并),這就容易導(dǎo)致實際的計算量更大,耗時較久。在Hologres V1.3版本針對上面的情況進行優(yōu)化,保證了生成的執(zhí)行計劃能夠利用Clustering Keys的有序性,并能保障跨Shuffle保序,從而提高查詢性能。但要注意:
當表沒有對Clustering Keys做過濾時,默認走的是SeqScan,而不是IndexScan(只有IndexScan才會利用Clustering Keys的有序?qū)傩裕?/p>
優(yōu)化器并不保障總是生成基于Clustering Keys有序的執(zhí)行計劃,因為利用Clustering Keys有序性是有些代價的(文件內(nèi)有序但內(nèi)存中需要額外排序的)。
示例如下。
表的DDL如下。
V2.1版本起支持的語法:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys; CREATE TABLE test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys ( a int NOT NULL, b int NOT NULL, c text ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a', clustering_key = 'a,b' ); INSERT INTO test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys SELECT i%500, i%100, i::text FROM generate_series(1, 1000) as s(i); ANALYZE test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys;所有版本支持的語法:
DROP TABLE if exists test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys; BEGIN; CREATE TABLE test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys ( a int NOT NULL, b int NOT NULL, c text ); CALL set_table_property('test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys', 'distribution_key', 'a'); CALL set_table_property('test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys', 'clustering_key', 'a,b'); COMMIT; INSERT INTO test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys SELECT i%500, i%100, i::text FROM generate_series(1, 1000) as s(i); ANALYZE test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys;查詢語句。
explain select * from test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys where a > 100 order by a, b;執(zhí)行計劃對比
V1.3之前版本(V1.1)的執(zhí)行計劃(執(zhí)行
explainSQL)如下。Sort (cost=0.00..0.00 rows=797 width=11) -> Gather (cost=0.00..2.48 rows=797 width=11) Sort Key: a, b -> Sort (cost=0.00..2.44 rows=797 width=11) Sort Key: a, b -> Exchange (Gather Exchange) (cost=0.00..1.11 rows=797 width=11) -> Decode (cost=0.00..1.11 rows=797 width=11) -> Index Scan using holo_index:[1] on test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=797 width=11) Cluster Filter: (a > 100)V1.3版本的執(zhí)行計劃如下。
Gather (cost=0.00..1.15 rows=797 width=11) Merge Key: a, b -> Exchange (Gather Exchange) (cost=0.00..1.11 rows=797 width=11) Merge Key: a, b -> Decode (cost=0.00..1.11 rows=797 width=11) -> Index Scan using holo_index:[1] on test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys (cost=0.00..1.01 rows=797 width=11) Order by: a, b Cluster Filter: (a > 100)
V1.3版本的執(zhí)行計劃相較于之前版本,利用表Clustering Keys的有序性直接做歸并輸出,整個執(zhí)行可Pipeline起來,不用再擔(dān)心數(shù)據(jù)量大的時候排序慢的問題。從執(zhí)行計劃對比中可以看到,V1.3版本生成的是Groupagg,相比Hashagg,處理復(fù)雜度更低,性能會更好。
針對Clustering Keys做Join的場景(Beta)
Hologres在V1.3版本新增了SortMergeJoin類型,以保證生成的執(zhí)行計劃能夠利用Clustering Keys的有序性,減少計算量,從而提高性能。但需要注意:
當前該功能還處于Beta版本,默認不開啟,需要在Query前添加如下參數(shù)開啟。
-- 開啟merge join set hg_experimental_enable_sort_merge_join=on;當表沒有對Clustering Keys做過濾時,默認走的是SeqScan,而不是IndexScan(只有IndexScan才會利用Clustering Keys的有序?qū)傩裕?/p>
優(yōu)化器并不保障總是生成基于Clustering Keys有序的執(zhí)行,因為利用Clustering Keys有序性是有些代價的(文件內(nèi)有序但內(nèi)存中需要額外排序)。
示例如下。
表的DDL如下。
V2.1版本起支持的語法:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1; CREATE TABLE test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1 ( a int, b int, c text ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a', clustering_key = 'a,b' ); INSERT INTO test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1 SELECT i % 500, i % 100, i::text FROM generate_series(1, 10000) AS s(i); ANALYZE test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2; CREATE TABLE test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2 ( a int, b int, c text ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a', clustering_key = 'a,b' ); INSERT INTO test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2 SELECT i % 600, i % 200, i::text FROM generate_series(1, 10000) AS s(i); ANALYZE test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2;所有版本支持的語法:
drop table if exists test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1; begin; create table test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1 ( a int, b int, c text ); call set_table_property('test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1', 'distribution_key', 'a'); call set_table_property('test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1', 'clustering_key', 'a,b'); commit; insert into test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1 select i%500, i%100, i::text from generate_series(1, 10000) as s(i); analyze test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1; drop table if exists test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2; begin; create table test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2 ( a int, b int, c text ); call set_table_property('test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2', 'distribution_key', 'a'); call set_table_property('test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2', 'clustering_key', 'a,b'); commit; insert into test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2 select i%600, i%200, i::text from generate_series(1, 10000) as s(i); analyze test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2;查詢語句如下。
explain select * from test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1 a join test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2 b on a.a = b.a and a.b=b.b where a.a > 100 and b.a < 300;執(zhí)行計劃對比
V1.3之前版本(V1.1)的執(zhí)行計劃如下。
Gather (cost=0.00..3.09 rows=4762 width=24) -> Hash Join (cost=0.00..2.67 rows=4762 width=24) Hash Cond: ((test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1.a = test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2.a) AND (test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1.b = test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2.b)) -> Exchange (Gather Exchange) (cost=0.00..1.14 rows=3993 width=12) -> Decode (cost=0.00..1.14 rows=3993 width=12) -> Index Scan using holo_index:[1] on test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1 (cost=0.00..1.01 rows=3993 width=12) Cluster Filter: ((a > 100) AND (a < 300)) -> Hash (cost=1.13..1.13 rows=3386 width=12) -> Exchange (Gather Exchange) (cost=0.00..1.13 rows=3386 width=12) -> Decode (cost=0.00..1.13 rows=3386 width=12) -> Index Scan using holo_index:[1] on test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2 (cost=0.00..1.01 rows=3386 width=12) Cluster Filter: ((a > 100) AND (a < 300))V1.3版本的執(zhí)行計劃如下。
Gather (cost=0.00..2.88 rows=4762 width=24) -> Merge Join (cost=0.00..2.46 rows=4762 width=24) Merge Cond: ((test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2.a = test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1.a) AND (test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2.b = test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1.b)) -> Exchange (Gather Exchange) (cost=0.00..1.14 rows=3386 width=12) Merge Key: test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2.a, test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2.b -> Decode (cost=0.00..1.14 rows=3386 width=12) -> Index Scan using holo_index:[1] on test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2 (cost=0.00..1.01 rows=3386 width=12) Order by: test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2.a, test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys2.b Cluster Filter: ((a > 100) AND (a < 300)) -> Exchange (Gather Exchange) (cost=0.00..1.14 rows=3993 width=12) Merge Key: test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1.a, test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1.b -> Decode (cost=0.00..1.14 rows=3993 width=12) -> Index Scan using holo_index:[1] on test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1 (cost=0.00..1.01 rows=3993 width=12) Order by: test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1.a, test_use_sort_info_of_clustering_keys1.b Cluster Filter: ((a > 100) AND (a < 300))
V1.3版本的執(zhí)行計劃相較于之前版本的執(zhí)行計劃,利用Clustering Index的有序性,在Shard內(nèi)做歸并排序后直接進行SortMergeJoin,讓整個執(zhí)行Pipeline起來;可規(guī)避數(shù)據(jù)量大較大時,HashJoin需將Hash Side填充至內(nèi)存而導(dǎo)致的OOM問題。