點(diǎn)聚類系數(shù)
點(diǎn)聚類系數(shù)表示在無向圖中某節(jié)點(diǎn)與其相連節(jié)點(diǎn)之間聚集成團(tuán)的程度的一個系數(shù)(稠密度),目的在于比較群組的聚合緊密程度與其能夠達(dá)到的聚合緊密程度。點(diǎn)聚類系數(shù)組件能夠輸出各節(jié)點(diǎn)的相鄰節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù)量、稠密度及其對數(shù)。
算法說明
在無向圖中,點(diǎn)聚類系數(shù)表示計(jì)算每一個節(jié)點(diǎn)周圍的稠密度,星狀網(wǎng)絡(luò)稠密度為0,全連通網(wǎng)絡(luò)稠密度為1。
配置組件
方法一:可視化方式
在Designer工作流頁面添加點(diǎn)聚類系數(shù)組件,并在界面右側(cè)配置相關(guān)參數(shù):
參數(shù)類型 | 參數(shù) | 描述 |
字段設(shè)置 | 起始節(jié)點(diǎn) | 邊表的起點(diǎn)所在列。 |
終止節(jié)點(diǎn) | 邊表的終點(diǎn)所在列。 | |
參數(shù)設(shè)置 | 最大節(jié)點(diǎn)度 | 默認(rèn)值為500,如果節(jié)點(diǎn)度大于該值,則進(jìn)行抽樣。 |
執(zhí)行調(diào)優(yōu) | 進(jìn)程數(shù)量 | 作業(yè)并行執(zhí)行的節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù)。數(shù)字越大并行度越高,但是框架通訊開銷會增大。 |
進(jìn)程內(nèi)存 | 單個作業(yè)可使用的最大內(nèi)存量,單位:MB,默認(rèn)值為4096。 如果實(shí)際使用內(nèi)存超過該值,會拋出 | |
數(shù)據(jù)切分大小 | 數(shù)據(jù)切分的大小,單位:MB,默認(rèn)值為64。 |
方法二:PAI命令方式
使用PAI命令配置點(diǎn)聚類系數(shù)組件參數(shù)。您可以使用SQL腳本組件進(jìn)行PAI命令調(diào)用,詳情請參見場景4:在SQL腳本組件中執(zhí)行PAI命令。
PAI -name NodeDensity
-project algo_public
-DinputEdgeTableName=NodeDensity_func_test_edge
-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id
-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id
-DoutputTableName=NodeDensity_func_test_result
-DmaxEdgeCnt=500;參數(shù) | 是否必選 | 默認(rèn)值 | 描述 |
inputEdgeTableName | 是 | 無 | 輸入邊表名。 |
inputEdgeTablePartitions | 否 | 全表讀入 | 輸入邊表的分區(qū)。 |
fromVertexCol | 是 | 無 | 輸入邊表的起點(diǎn)所在列。 |
toVertexCol | 是 | 無 | 輸入邊表的終點(diǎn)所在列。 |
outputTableName | 是 | 無 | 輸出表名。 |
outputTablePartitions | 否 | 無 | 輸出表的分區(qū)。 |
lifecycle | 否 | 無 | 輸出表的生命周期。 |
maxEdgeCnt | 否 | 500 | 如果節(jié)點(diǎn)度大于該值,則進(jìn)行抽樣。 |
workerNum | 否 | 未設(shè)置 | 作業(yè)并行執(zhí)行的節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù)。數(shù)字越大并行度越高,但是框架通訊開銷會增大。 |
workerMem | 否 | 4096 | 單個作業(yè)可使用的最大內(nèi)存量,單位:MB,默認(rèn)值為4096。 如果實(shí)際使用內(nèi)存超過該值,會拋出 |
splitSize | 否 | 64 | 數(shù)據(jù)切分的大小,單位:MB。 |
使用示例
添加SQL腳本組件,輸入以下SQL語句生成訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)。
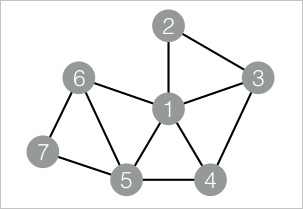
drop table if exists NodeDensity_func_test_edge; create table NodeDensity_func_test_edge as select * from ( select '1' as flow_out_id, '2' as flow_in_id union all select '1' as flow_out_id, '3' as flow_in_id union all select '1' as flow_out_id, '4' as flow_in_id union all select '1' as flow_out_id, '5' as flow_in_id union all select '1' as flow_out_id, '6' as flow_in_id union all select '2' as flow_out_id, '3' as flow_in_id union all select '3' as flow_out_id, '4' as flow_in_id union all select '4' as flow_out_id, '5' as flow_in_id union all select '5' as flow_out_id, '6' as flow_in_id union all select '5' as flow_out_id, '7' as flow_in_id union all select '6' as flow_out_id, '7' as flow_in_id )tmp; drop table if exists NodeDensity_func_test_result; create table NodeDensity_func_test_result ( node string, node_cnt bigint, edge_cnt bigint, density double, log_density double );對應(yīng)的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)圖:
添加SQL腳本組件,輸入以下PAI命令進(jìn)行訓(xùn)練。
drop table if exists ${o1}; PAI -name NodeDensity -project algo_public -DinputEdgeTableName=NodeDensity_func_test_edge -DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id -DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id -DoutputTableName=${o1} -DmaxEdgeCnt=500;右擊上一步的組件,選擇查看數(shù)據(jù) > SQL腳本的輸出,查看訓(xùn)練結(jié)果。
| node | node_cnt | edge_cnt | density | log_density | | ---- | -------- | -------- | ------- | ----------- | | 1 | 5 | 4 | 0.4 | 1.45657 | | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.0 | 1.24696 | | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0.66667 | 1.35204 | | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0.66667 | 1.35204 | | 5 | 4 | 3 | 0.5 | 1.41189 | | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0.66667 | 1.35204 | | 7 | 2 | 1 | 1.0 | 1.24696 |